Running applications on individual systems cause resource wastage. Virtualization provides a solution to this issue. In fact, virtualization is the process of creating a virtual version of a server, operating system, network or a storage device. It also divides resources between multiple execution environments. Moreover, a hypervisor is related to virtualization. It is a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM). In other words, it creates and runs virtual machines. There are two types of hypervisors as Type 1 and Type 2.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is Type 1 Hypervisor
– Definition, Functionality
2. What is Type 2 Hypervisor
– Definition, Functionality
3. Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor
– Comparison of Key Differences
Key Terms
Bare Metal Hypervisor, Host OS Hypervisor, Native Hypervisor, Type 1 Hypervisor, Type 2 Hypervisor, Virtual Machine, Virtualization
What is Type 1 Hypervisor
A computer on which the hypervisor runs single or multiple virtual machines is called a host machine. In addition, each virtual machine is a guest machine. Type 1 Hypervisor is called a Bare Metal Hypervisor or native Hypervisor. It runs directly on the host hardware. Furthermore, it manages the guest operating systems and controls hardware.
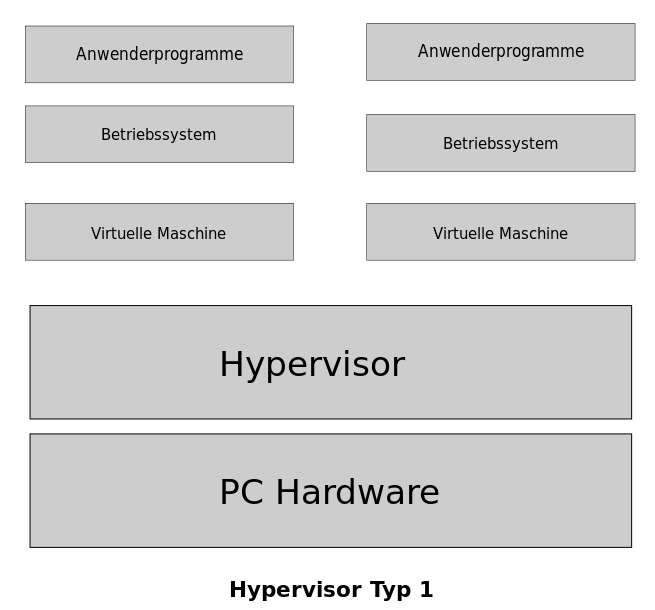
Moreover, the first hypervisors developed by IBM were native hypervisors. These included SIMMON test software. Furthermore, it also had CP/CMS operating system. AntsleOs, Xen, XCP-ng, Microsoft Hyper V, VMware ESX/ESXi, Oracle VM Server for x86 are some examples for Type 1 Hypervisors.
What is Type 2 Hypervisor
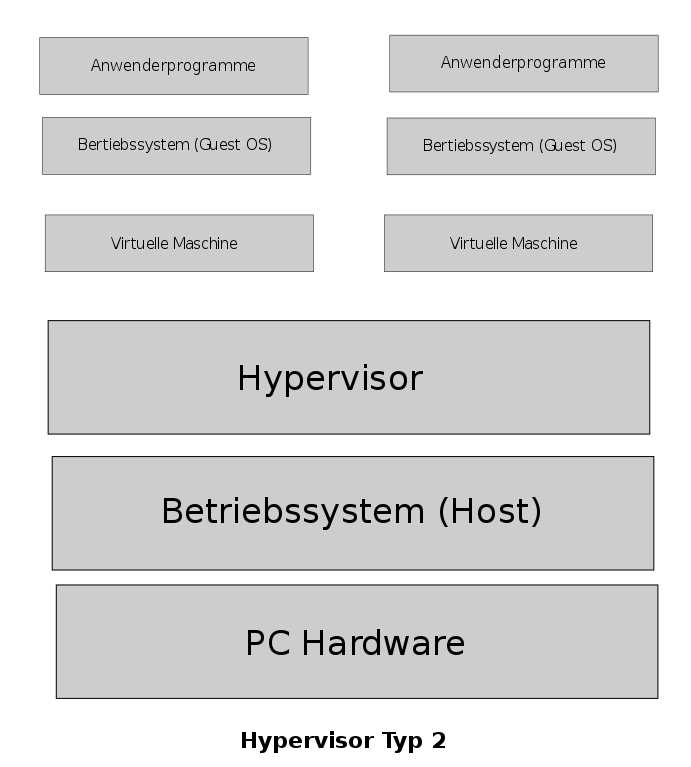
Type 2 Hypervisor is called a Host OS Hypervisor. These hypervisors execute on an operating system similar to other computer programs. For example, assume that there is an operating system. There is a hypervisor on top of the OS. It provides an emulator environment to run another operating system. In other words, a guest operating system runs as a process on the host. Moreover, VMware Workstation, VMware Player, VirtualBox, Parallel Desktop for Mac are some examples for Type 2 Hypervisors.
Difference Between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor
Definition
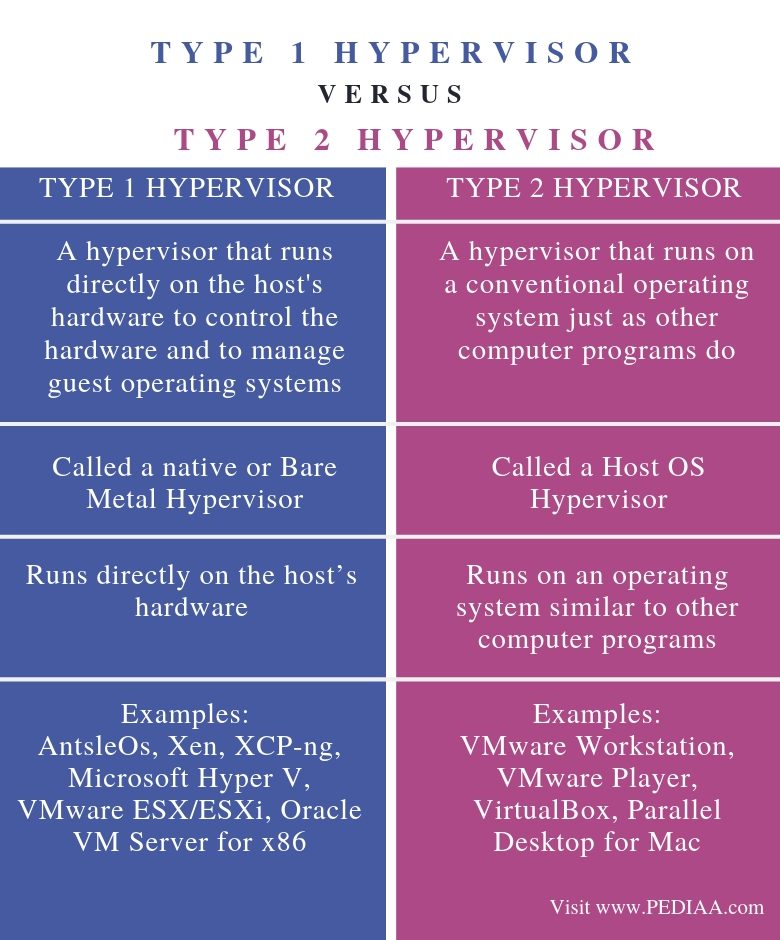
Type 1 hypervisor is a hypervisor that runs directly on the host’s hardware to control the hardware and to manage guest operating systems while Type 2 hypervisors run on a conventional operating system just as other computer programs do. Thus, this is the main difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor.
Synonyms
Type 1 Hypervisor is called a native or Bare Metal Hypervisor while type 2 Hypervisor is called a Host OS Hypervisor.
Functionality
Functionality is another difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor. Type 1 Hypervisor runs directly on the host’s hardware while Type 2 Hypervisor runs on an operating system similar to other computer programs.
Examples
AntsleOs, Xen, XCP-ng, Microsoft Hyper V, VMware ESX/ESXi, Oracle VM Server for x86 are some examples for Type 1 Hypervisors while VMware Workstation, VMware Player, VirtualBox, Parallel Desktop for Mac are some examples for Type 2 Hypervisors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Hypervisor is capable of creating and executing virtual machines. There are two types of hypervisors as Type 1 and Type 2. The main difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Hypervisor is that Type 1 Hypervisor runs directly on the host’s hardware while Type 2 Hypervisor runs on an operating system similar to other computer programs.
References:
1.“Hypervisor.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 11 Apr. 2019, Available here.
2.edureka! VMware Tutorial For Beginners | VMware Workstation | VMware Virtualization | Edureka, Edureka!, 25 June 2018, Available here.
No comments:
Post a Comment